
FinnoUgric languages map J. r. r. tolkien
Finno-Ugric can first be divided into the most distantly related Ugric and Finnic (sometimes called Volga-Finnic) groups, which may have separated as long ago as five millennia. Within these, three relatively closely related groups of languages are found: the Baltic-Finnic, the Permic, and the Ob-Ugric.

Songs And Music Of Finno Ugric Languages YouTube
The Volga Finns (sometimes referred to as Eastern Finns) [1] are a historical group of indigenous peoples of Russia living in the vicinity of the Volga, who speak Uralic languages.

FinnoUgric Peoples FennoUgria
Finno-Ugric ( / ˌfɪnoʊˈjuːɡrɪk / or / ˌfɪnoʊˈuːɡrɪk /; Fenno-Ugric) [1] or Finno-Ugrian ( Fenno-Ugrian) is a traditional grouping of all languages in the Uralic language family except the Samoyedic languages.
Alternative Linguiatics The Expansion of the FinnoUgric Peoples
The Uralic language family in its current status consists of two related groups of languages, the Finno-Ugric and the Samoyedic, both of which developed from a common ancestor, called Proto-Uralic, that was spoken 7,000 to 10,000 years ago in the general area of the north-central Ural Mountains.

Baltic & FennoUgric Languages Wiki Languages Amino
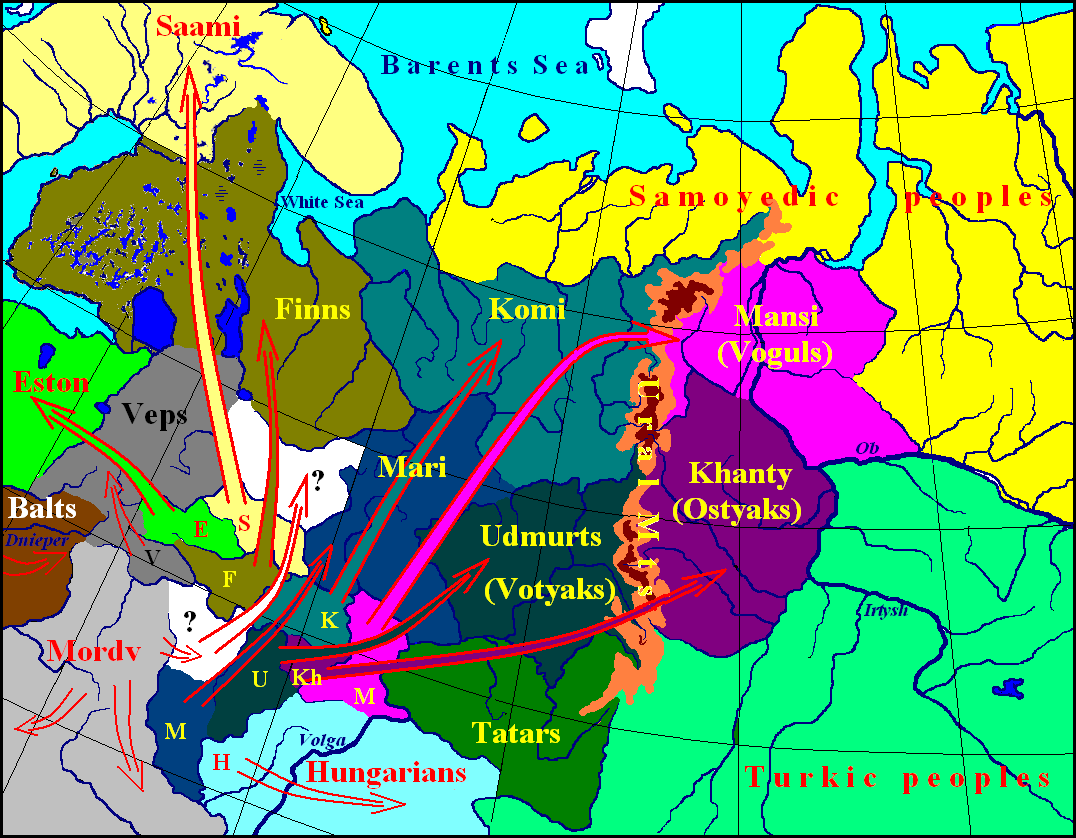
The Finno-Ugric peoples settled in the 6th to 4th millennium B.C. around the Ural Mountains, mainly on their eastern side, and the river Ob. Individual groups set out between 4000 and 3000 B.C. in an easterly and westerly direction. The Ugric branch of the Finno-Ugric language family is composed of the languages of the two Ugric peoples Khanty.

Digitization project on textual materials of FinnoUgric population groups Minorities Records
The Finno-Ugric languages are a fascinating linguistic group of the Uralic language family that spans across Northern Eurasia. These languages are unique in their own right, with distinctive features and characteristics that set them apart from other language families.
13 Fascinating Facts about the Hungarian Language
Finno-Ugric ( / ˌfɪnoʊˈjuːɡrɪk / or / ˌfɪnoʊˈuːɡrɪk /; Fenno-Ugric) [1] or Finno-Ugrian ( Fenno-Ugrian) is a traditional grouping of all languages in the Uralic language family except the Samoyedic languages.

FennoUgrian languages Language map, Map, Historical maps
The Research Unit for Volgaic Languages, which operates under Finno-Ugric Languages, co-ordinates our research projects. Hungarian, especially its lexicon, phraseology and language teaching, is also studied at Finno-Ugric Languages. Our themes for research include, for example. Lexicon in the languages of the Volga region.

Happy FinnoUgric Day. Saturday 17 October 2020 is celebrated… by Adam Rang Estonian Saunas
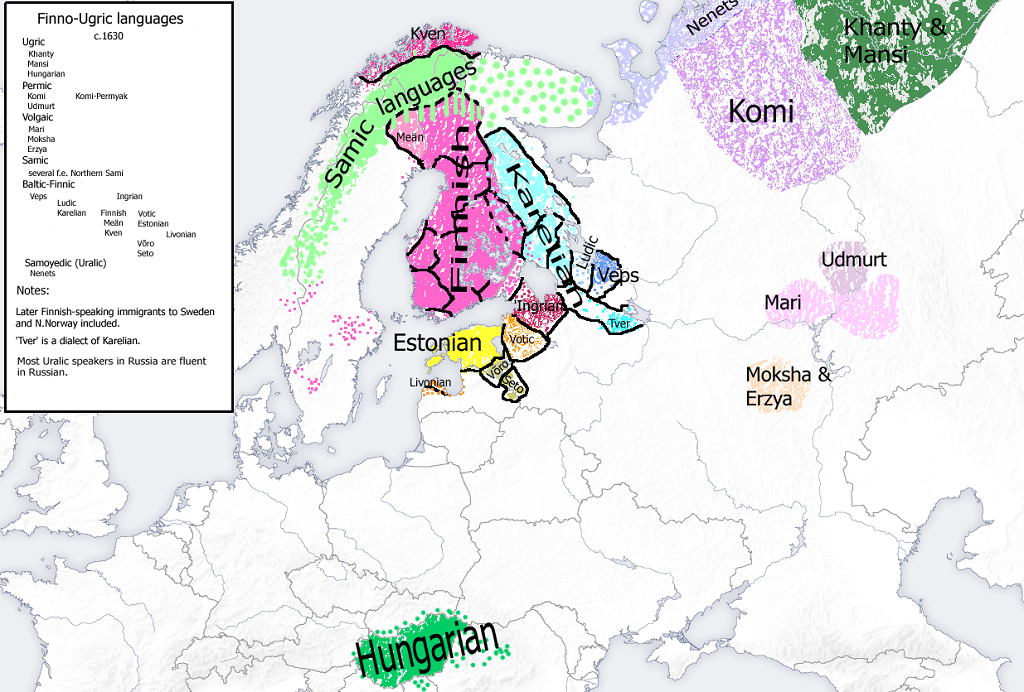
The Ugric division of Finno-Ugric languages is composed of Hungarian and the Ob-Ugric languages Mansi (Vogul) and Khanty (Ostyak). The Finnic division of Finno-Ugric languages is composed of five groups. The Baltic-Finnic group consists of Finnish, Estonian, Karelian (including Olonets), Ludic, Veps, Ingrian, Livonian, and Votic.

Finnish language 💬🇫🇮 FinnoUgric language tree and unique words YouTube
The Ob-Ugric languages are spoken in the region of the Ob and Irtysh rivers in central Russia. They had no written tradition or literary language until 1930; since 1937 they have been written in a modified Cyrillic alphabet but have developed no important literature and are little used in government or education. See also Finno-Ugric languages.

Finnougrische Sprachen YouTube
The early Finno-Ugric system of vowels most likely possessed quantitative vowel contrasts (long versus short, or full versus reduced). Such contrasts are present in Baltic-Finnic, Sami, and Ugric and within Samoyedic—e.g., Finnish tulen 'of fire' and tuulen 'of wind,' tuleen 'into fire,' and tuuleen 'into wind'; Hungarian szel 'slice' and szél 'wind,' szelet 'wind.

The FinnoUgric Languages The Disappearing Heritage of Mankind YouTube
The Finno-Ugric language kinship was proven in the seventeenth century, while cooperation in the sphere of Finno-Ugric linguistics has begun in the nineteenth century. Later, these contacts led to the development of the discipline of Finno-Ugric Studies where linguistics, history, ethnography, and archeology were the key..

PPT Word order in FinnoUgric languages PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3431523
Finno-Ugrian language studies is a discipline that examines the structure and history of Finno-Ugrian languages, giving consideration to both the methodological starting points developed by general linguistics and the special characteristics of the material and spiritual culture of the peoples that speak these languages.

The FinnoUgric languages From the north to the south YouTube
As the name suggests, the Finno-Ugric family consists of two major branches: Finnic languages and Ugric languages. The former branch includes Finnish, as well as Estonian, Saami, Komi, Mordvin, Udmurt, Mari and several other smaller languages such as Karelian, Votic, Veps and Livonian.

FinnoUgric languages Wikiwand
The Uralic (Finno-Ugric) languages, the second largest language family in Europe, including three European nation-state languages (Hungarian, Finnish, Estonian) and a number of minority languages in Northern Eurasia, look back to a long history of research.

Mulgimaa takes centre stage as Estonia embraces its FinnoUgric family
Finno-Ugric is sometimes used as a synonym for Uralic, [2] though Finno-Ugric is widely understood to exclude the Samoyedic languages. [3] Scholars who do not accept the traditional notion that Samoyedic split first from the rest of the Uralic family may treat the terms as synonymous. [4] History Homeland